Many pool owners face issues like murky water and damaged equipment. These problems often stem from not understanding water chemistry. Learning about alkalinity vs pH can turn your pool into a clear and inviting place. It’s all about keeping the water quality right.

I’ll explain the science behind alkalinity and pH levels. You’ll see how they affect your pool’s health. Knowing this can help you avoid expensive problems and ensure a great swimming experience every time.
Understanding Basic Pool Water Chemistry
Diving into pool maintenance means mastering the world of water chemistry. Every pool needs a balance of chemicals for a safe swim. My years of experience show that knowing these basics is key for pool owners.
Water chemistry is more than just a pretty pool. It’s about creating a safe space for swimmers and protecting equipment. The mix of chemicals affects your pool’s health.
The Critical Balance of Chemical Parameters
Several key factors are important for pool water chemistry:
- pH levels (ideal range between 7.2 and 7.8)
- Total alkalinity (recommended 80-120 ppm)
- Chlorine concentration
- Calcium hardness
Advanced Chemical Interactions
Knowing about advanced chemical processes helps manage water quality. High alkalinity helps prevent pH changes that could harm your pool.
Impact on Pool Health
Unbalanced water chemistry can cause many problems, including:
- Corrosion of pool equipment
- Skin and eye irritation for swimmers
- Reduced chlorine effectiveness
- Potential algae growth
Keeping the right chemical balance ensures a safe, clean swim for all.
Read also: Pool Equipment Enclosure Kits
Defining pH in Pool Water
Understanding pH is key to keeping pool water healthy. pH measures the acid in water, showing hydrogen ion levels. For pool owners, knowing pH ensures water quality and swimmer comfort.
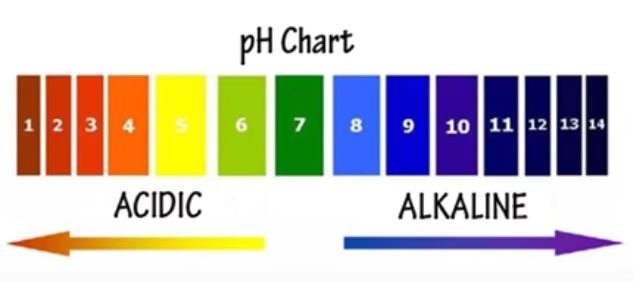
The best pH range for pool water is 7.2 to 7.8, with 7.4-7.6 being ideal. This range is close to the pH of human eyes and mucous membranes. It makes swimming more comfortable and safe.
Different types of water have unique pH levels. Let’s compare:
- Drinking water: typically ranges from 6.5 to 8.5
- Pool water: optimal range 7.2-7.8
- Human tears: around 7.4
Proper pH balance is important. It helps neutralize acids and bases. If pH levels get too high or low, water can become corrosive or form scales. This can damage pool equipment and irritate swimmers’ skin and eyes.
| pH Level | Water Characteristics | Impact on Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Below 7.0 | Acidic | Corrosive to equipment |
| 7.2-7.8 | Balanced | Optimal swimming conditions |
| Above 8.0 | Alkaline | Scale formation and reduced chlorine effectiveness |
Regular testing and careful management of your pool’s pH are vital. They ensure a safe, comfortable swimming environment for everyone.
The Science Behind Water Alkalinity
Knowing about water alkalinity is key for a healthy swimming pool. As a pool owner, I’ve found that alkalinity is vital. It acts as a shield for your pool’s balance.
Water alkalinity is a complex idea. It measures how well water can handle acids. It’s like a defense system for your pool’s water, keeping it stable and comfy.
Types of Alkalinity in Pool Water
Pool water has different kinds of alkalinity, each with its own job:
- Carbonate alkalinity: Primary buffer in pool water
- Bicarbonate alkalinity: Most common form of alkalinity
- Hydroxide alkalinity: Less frequent but significant
How Alkalinity Acts as a Buffer
Alkalinity is more than just a chemical number. It’s a key part that stops pH from changing too fast. When acids come in, alkalinity fights them off, keeping the water chemistry steady.
Measuring Total Alkalinity
Experts say to keep total alkalinity between 80-120 parts per million (ppm). This range keeps the pool water balanced. It also protects swimmers and pool equipment from harm.
| Alkalinity Level | Pool Water Condition |
|---|---|
| Below 80 ppm | Unstable pH, possible corrosion |
| 80-120 ppm | Ideal balanced water |
| Above 120 ppm | Scale formation, less effective chlorine |
By getting water alkalinity, you can keep your pool clean and healthy.
Alkalinity VS pH: Understanding the Differences
It can be hard for pool owners to tell the difference between alkalinity and pH. Even though they seem alike, each plays a special part in keeping your pool healthy.
Read also: How to Neutralize Muriatic Acid
The pH scale goes from 0 to 14. It shows how acidic or alkaline a solution is. Water below 7 is acidic, and water above 7 is alkaline. For pools, the best pH is between 7.2 and 7.8.
- pH measures the concentration of hydrogen ions
- Alkalinity measures the water’s ability to neutralize acids
- Both are critical for balanced pool water chemistry
Alkalinity helps keep the pH stable. It’s measured in parts per million (ppm) and should be 80-120 ppm for pools. Think of alkalinity as a shock absorber for your pool’s chemical balance.
If alkalinity is too low, your pool’s pH can swing wildly. This can damage pool equipment and make swimming uncomfortable. On the other hand, too much alkalinity makes it hard to adjust pH levels.
Knowing these differences helps you keep your pool water chemistry perfect. This ensures a safe and fun swimming experience.
Effects of Unbalanced pH Levels
Keeping your pool water chemistry right is key to protecting your investment and keeping swimmers safe. Unbalanced pH levels can mess up your pool’s whole system. This causes problems that go beyond just water quality.
When pH levels are off, many parts of your pool experience suffer. Let’s look at the main areas affected by pH imbalances.
Impact on Pool Equipment
Wrong pH levels can quietly harm your pool’s setup. Acidic water speeds up corrosion on equipment. This means your expensive pool parts like pumps and heaters can wear out fast.
- Acidic water corrodes metal components
- Liner materials break down faster
- Expensive equipment needs early replacement
Swimmer Comfort and Safety
pH testing is not just for equipment – it affects swimmer health too. Unbalanced water can make swimmers uncomfortable and even risk their health.
- Low pH causes eye and skin irritation
- High pH leads to itchy skin
- Increased risk of bacterial growth
Chlorine Efficiency
The importance of alkalinity shines when we talk about chlorine. Extreme pH levels make chlorine less effective at keeping your pool clean.
At high pH levels, chlorine doesn’t work well. This leaves your pool open to germs. On the other hand, low pH levels make chlorine disappear fast, risking water safety.
Regular tests for alkalinity and pH are your best defense. Keeping your pool safe means watching your water chemistry closely.
Consequences of Improper Alkalinity
Understanding the balance between alkalinity and pH in swimming pools is key. It prevents serious problems. Low and high alkalinity levels can harm your pool’s health and performance.

Low alkalinity in water is dangerous for pool owners. The pH becomes unstable, leading to quick and unpredictable changes. This can damage pool surfaces and equipment.
- Potential risks of low alkalinity include:
- Corrosion of metal pool components
- Etching of pool surfaces
- Increased swimmer discomfort
High alkalinity also poses challenges. It makes adjusting pH very hard. This can lead to scaling on surfaces, less effective chlorine, and cloudy water.
| Alkalinity Level | Water Quality Impact | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low Alkalinity (Below 80 ppm) | Unstable pH, equipment damage risk | Add alkalinity increaser |
| High Alkalinity (Above 180 ppm) | Scaling, less effective chlorine | Use pH reducer and alkalinity decreaser |
Keeping alkalinity in check is vital for your pool’s health. Regular testing and careful chemical management can prevent these issues. This ensures a safe and comfortable swimming environment.
Testing and Monitoring Methods
Keeping your pool water chemistry right is key. I’ll show you how to test and monitor it. Knowing how to check for high alkalinity and carbonic acid is important.
There are many ways to test pool water, from easy DIY tests to complex professional ones. Each method gives you important info about your pool’s chemicals. This helps avoid big problems.
Professional Testing Equipment
Professional tests give a detailed look at your pool’s water. They use special tools to spot small changes in chemical levels. Some top professional tests include:
- Digital spectrophotometer analysis
- Laboratory water testing services
- Advanced reverse osmosis water quality testing
DIY Testing Options
If you own a pool at home, there are simple tests to check the water:
- Test strips for quick checks
- Digital pool water testing kits
- Liquid reagent test kits
| Testing Method | Accuracy | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Test Strips | Low-Medium | $10-$20 |
| Digital Kits | High | $50-$100 |
| Professional Lab Test | Very High | $50-$150 |
Frequency of Testing
Test your pool water once a week when it’s in use. Changes like heavy use or weather can affect the water. Knowing about alkalinity and carbonic acid helps keep the water right.
Testing often keeps your pool safe and fun. It also stops damage to your pool equipment. This makes swimming a great experience.
Adjusting Pool pH Levels Safely
Keeping your pool’s pH levels right is key. You need to know how much acid to add and how your pool can handle it. It’s like managing the chemistry of drinking water, but for your pool. This ensures the water is safe and comfortable for swimmers.
For adjusting pH levels, you’ll need the right chemicals:
- To lower high pH: Use muriatic acid or sodium bisulfate
- To raise low pH: Apply soda ash (sodium carbonate)
- Always add chemicals to water, never water to chemicals
Handling pool chemicals safely is very important. I suggest wearing protective glasses and gloves. Follow these steps:
- Test current pH levels with a reliable testing kit
- Calculate the exact amount of chemical needed
- Dilute chemicals according to manufacturer instructions
- Add chemicals slowly and evenly across the pool
- Wait 4-6 hours before retesting
| pH Level | Action Required | Chemical to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Below 7.2 | Raise pH | Soda Ash |
| Above 7.8 | Lower pH | Muriatic Acid |
Good pool maintenance means knowing how chemicals work together. By following these tips, you’ll keep your pool water perfect for swimming.
Managing Total Alkalinity in Your Pool
Keeping the right water alkalinity is key for a great pool. As a pool owner, knowing how to manage total alkalinity can save you time and money. It also prevents headaches later on.
The alkalinity definition is more than just a number. It’s a vital chemical buffer. It helps keep your pool’s pH levels stable and protects your equipment from damage.
Essential Products for Alkalinity Adjustment
Here are the must-have products for managing water alkalinity:
- Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) for raising alkalinity
- Muriatic acid for lowering alkalinity
- Alkalinity increaser solutions
- pH testing kits
Best Practices for Chemical Addition
Follow these safe guidelines when adjusting your pool’s chemistry:
- Always test water alkalinity and pH levels before adding chemicals
- Add chemicals slowly and in small amounts
- Distribute chemicals evenly across the pool
- Wait 4-6 hours between chemical treatments
- Retest water after each adjustment
The ph definition is closely tied to alkalinity. A balanced pool usually has an alkalinity level between 80-120 parts per million (ppm). By managing these levels well, you’ll have clear water and protect your pool.
Seasonal Variations and Water Chemistry
Keeping your pool’s water chemistry right all year is key. Each season brings its own set of challenges that can change your pool’s ph scale and balance. Knowing these changes helps you keep your pool water perfect.

Summer is the toughest time for pool chemistry. The heat and more swimmers make water chemistry harder to manage. Alkaline water can quickly change pH in summer. Heat, sunlight, and lots of use cause big changes in your pool’s chemicals.
- Summer: Highest chemical maintenance requirements
- Spring: Initial water balancing after winter
- Fall: Preparation for pool closure
- Winter: Minimal chemical interactions
Rain and weather also affect your pool’s water. Acidic water can come from rain, and dry times can raise alkalinity. I suggest testing your pool water weekly when it’s busy to keep it balanced.
| Season | pH Level Impact | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Summer | Rapid pH fluctuations | Frequent testing, chemical adjustments |
| Spring | Unstable chemistry | Complete water reset, balanced chemicals |
| Fall | Decreasing chemical activity | Gradual chemical reduction |
| Winter | Minimal chemical interactions | Periodic monitoring |
Understanding seasonal changes helps you manage your pool’s water chemistry better. Regular checks and quick fixes keep your pool safe and fun all year.
Common Chemical Treatment Mistakes
Keeping your pool water perfect can be hard. I’ve seen many pool owners make big mistakes. It’s key to know how to test alkalinity and ph levels to avoid these errors.
Many pool owners make water balance problems without knowing it. They make mistakes with chemical treatment. These errors can hurt the pool’s health and make swimming uncomfortable.
- Overusing chemicals without proper alkalinity testing
- Neglecting regular ph testing
- Ignoring total alkalinity importance
- Failing to understand water chemistry interactions
Chemical treatment needs to be done carefully. Adding chemicals without a plan can mess up your pool’s balance. I suggest making a plan for keeping your water clean.
Read also: How to Clean Water Pipes in Your House
| Mistake | Potential Consequence | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent Testing | Unstable Water Chemistry | Weekly Professional Testing |
| Chemical Overdosing | Equipment Damage | Precise Measurement |
| Ignoring Total Alkalinity | pH Fluctuations | Regular Alkalinity Checks |
To keep your pool in top shape, you need to understand how all chemicals work together. Don’t just focus on one thing. A complete approach will keep your pool water perfect.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you’ll keep your pool equipment safe. You’ll also make swimming safer and more fun for everyone.

Conclusion
Knowing how alkalinity and pH levels work together is key to keeping your pool water top-notch. We’ve looked into how this balance keeps your pool water safe and inviting.
Alkalinity in water is like a shield for your pool’s health. By getting the chemistry right, you avoid damage to equipment and ensure a comfortable swim. Regular checks and adjustments are essential to keep this balance.
We’ve covered the science of water chemistry, from how to test it to how it changes with the seasons. Now, you’re ready to handle pool care like a pro. Keep up the good work to keep your pool water sparkling and ready for fun.
Your pool is a big investment, and it’s worth taking care of. By understanding alkalinity and pH, you’ll make your swimming experience safe and refreshing. Start pool maintenance with confidence, knowing you can keep your water just right.


